Tungsten Alloy Crankshafts
Structure of Tungsten Alloy Crankshaft
(1)Antiscuffing. The bearing surface should be able to absorb enough oil to keep it from scuffing during startup, or any other time when it must run momentarily without an oil supply.
(2) Embedabillty. The surface of the bearing must be soft enough to allow particles of foreign matter to embed themselves and prevent damage of the shaft journal.
(3) Conformability. The bearing must be able to conform or fit itself to the surface of the crankshaft Journal.
(4) Conductivity. The bearings must be able to conduct heat to the connecting rod so that they will not overheat.
(5) Resistance to Heat. The bearing must be able to maintain all of these characteristics throughout its entire operating temperature range.
a. Connecting Rod Lubrication. The connecting rod bearings fit into the lower end of the connecting rod. They are fed a constant supply of oil through a hole In the crankshaft Journal. A hole in the upper bearing half feeds a passage In the connecting rod to provide oil to the piston pin.
b. Crankshaft Main Bearings (Fig. 3-44). The upper halves of the main bearings fit right into the crankcase, and the lower halves fit into the caps that hold the crankshaft in place. The main bearings have holes drilled in their upper halves through which a supply of oil is fed to them. The tungsten alloy crankshaft has holes drilled in the journals that receive oil from the main bearings to feed the rod bearings. It is a common practice to cut a groove In the center of the main bearing Inserts. This supplies a more constant supply of oil to the connecting rod bearings. One of the main bear- Ings also serves as a thrust bearing. This controls back and forth movement of the crankshaft. This thrust bearing Is characterized by side flanges.
General. The flywheel stores energy from the power strokes, and smoothly delivers it to the drive train of the vehicle. It mounts on the end of the crankshaft, between the engine and the transmission.
b. Manual Transmission. When the vehicle Is equipped with a manual transmission, the fly- wheel serves to mount the clutch.
Automatic Transmission. When the vehicle Isequipped with an automatic transmission, the flywheel serves to support the front of the torque converter. On some configurations, the flywheel is combined with the torque converter.
d. Starter Ring Gear. The outer edge of the flywheel Is lined with gear teeth. They are to engage the drive gear on the starter motor.
e. Construction. The flywheel on large, low- speed engines usually is made of cast iron. This Is desirable due to the heavy weight of the cast Iron, which helps the engine maintain a steady speed. Small, high-speed engines usually use a forged steel or forged aluminum flywheel for the following reasons.
(1) The cast iron is too heavy, giving it too much inertia to allow the speed variations necessary on small engines.
(2) Cast iron, because of its weight, will pull itself apart at high speeds due to centrifugal force.
What is Tungsten Alloy Crankshaft?
The crankshaft, sometimes casually abbreviated to crank, is the part of an engine which translates reciprocating linear piston motion into rotary motion. To convert the reciprocating motion into rotation, the tungsten alloy crankshaft has "crank throws" or "crankpins", additional bearing surfaces whose axis is offset from that of the crank, by which the "big ends" of the connecting rod for each cylinder attaches and imparts its downward motion into the shaft.
It typically connects to a flywheel, to reduce the pulsation characteristic of the four-stroke cycle, and sometimes a torsional or vibrational damper at the opposite end, to reduce the torsion vibrations often caused along the length of the tungsten alloy crankshaft by the cylinders farthest from the output end acting on the torsional elasticity of the metal.
 |
 |
| Tungsten Alloy Crankshaft Components | Tungsten Alloy Crankshaft-01 |
 |
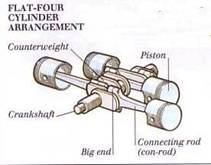 |
| Tungsten Alloy Crankshaft-02 | Tungsten Alloy Crankshaft Picture |
Tungsten Heavy Alloy is superior to lead in terms of durability, dimensional stability, high density, well wearing resistance and low toxicity.
Therefore, tungsten alloy products are used extensively to balance crankshafts in high performance engines. Individual weights are stocked.
So if you have any interest in tungsten alloy crankshaft, please feel free to email us: sales@chinatungsten.com, sales@xiamentungsten.com or call us by: 0086 592 512 9696, 0086 592 512 9595.






 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com